6.00.1x - Week 1
1.1 Introduction:
Machine are good at calculations and remember results.
Some problems require better algorithm to solve faster.
Some problems are fundamentally hard:turing halting or decrypt encryption which is benefical for us.
Machine are good at calculations and remember results.
Some problems require better algorithm to solve faster.
Some problems are fundamentally hard:turing halting or decrypt encryption which is benefical for us.
1.1 Knowledge
Declarative knowledge: statement of fact
Imperative knowledge: recipe, how to solve
Algorithm = sequence of steps + flow of control + when/how to stop
Declarative knowledge: statement of fact
Imperative knowledge: recipe, how to solve
Algorithm = sequence of steps + flow of control + when/how to stop
1.2 Machines
Fixed program vs. Stored program
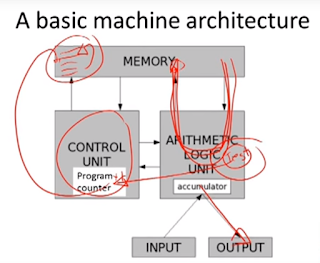
Core of machine: Memory, Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), and Control Unit with program counter
Interpreter vs Compiler: read 1
Turing machine: infinite tape, 6 primitives: move left, move right, scan, read, write, do nothing
Anything computable in one language is computable in any other programming language
1.3 Languages
Expression: legal combination of primitives
Syntax: combination of primitives that makes sense, legal expression
Static semantics: valid syntax that has meaning
Semantic: meaning associated with a syntactically correct expression with no static semantic errors
Reference: Quora, read 1
1.4 Types
Program: sequence of definitions and commands
Commands (statements): instruct interpreter to do something
Objects: scalar (can't be subdivided) or non-scalar (have internal structured)
Scalar objects: int, float, bool, NoneType
Division will return float
Operation precedence: **, * or / or //, + or -, left to right
1.5 Variables
Can bind (assign) and re-bind (re-assign) variable names
In programming, you do not "solve for x"
1.6 Operators and Branching
if, elif, else
2.1 Bindings
keywords - will have a different color when typed in IDE
2.2 Strings
String is non-scalar object. Casting: str(2.5) = '2.5'
letters, special characters, spaces, digits in single quotes or double quotation marks
3 * 'eric' = 'ericericeric'
len('eric') = 4, 'eric'[0] = 'e', 'eric'[1:3] = 'ri' (excluding last index), 'eric'[:3] = 'eri', 'eric'[1:] = 'ric'
'eric'[:] = 'eric' (a copy, not original string), 'a' in 'hat' = True
string[start:stop:step]
2.3 Input/Output
text = input("whatever typed will be saved into text")
2.4 IDEs
Spyder (comes with Anaconda) - shortcut F5 to Run
2.5 Control Flow
while vs for loops: can rewrite a for loop using a while loop, the other way not always correct
range(5): 0 to 4 - up to but not including. range(5, 7) = 5, 6. range(0, 6, 2) = 0, 2, 4
break vs continue
del(str): clear whatever value attached to str
Ctrl + c: to stop infinite loop
1.4 Types
Program: sequence of definitions and commands
Commands (statements): instruct interpreter to do something
Objects: scalar (can't be subdivided) or non-scalar (have internal structured)
Scalar objects: int, float, bool, NoneType
Division will return float
Operation precedence: **, * or / or //, + or -, left to right
1.5 Variables
Can bind (assign) and re-bind (re-assign) variable names
In programming, you do not "solve for x"
1.6 Operators and Branching
if, elif, else
2.1 Bindings
keywords - will have a different color when typed in IDE
2.2 Strings
String is non-scalar object. Casting: str(2.5) = '2.5'
letters, special characters, spaces, digits in single quotes or double quotation marks
3 * 'eric' = 'ericericeric'
len('eric') = 4, 'eric'[0] = 'e', 'eric'[1:3] = 'ri' (excluding last index), 'eric'[:3] = 'eri', 'eric'[1:] = 'ric'
'eric'[:] = 'eric' (a copy, not original string), 'a' in 'hat' = True
string[start:stop:step]
2.3 Input/Output
text = input("whatever typed will be saved into text")
2.4 IDEs
Spyder (comes with Anaconda) - shortcut F5 to Run
2.5 Control Flow
while vs for loops: can rewrite a for loop using a while loop, the other way not always correct
range(5): 0 to 4 - up to but not including. range(5, 7) = 5, 6. range(0, 6, 2) = 0, 2, 4
break vs continue
del(str): clear whatever value attached to str
Ctrl + c: to stop infinite loop


Comments
Post a Comment